In more than 25 years since its founding, the Leibniz Centre for Tropical Marine Research (ZMT) has developed and strengthened its network of partners in Germany and abroad. The participation of ZMT employees in national and international organisations contributes to the integration of German marine tropical ecology research with international programmes and the development of common strategies.
Membership in the following national organisations and alliances

Leibniz Association
They conduct basic and applied research, including in the interdisciplinary Leibniz Research Alliances, maintain scientific infrastructure, and provide research-based services. The Leibniz Association identifies focus areas for knowledge transfer, particularly with the Leibniz research museums. It advises and informs policymakers, science, industry and the general public. Leibniz institutions collaborate intensively with universities – including in the form of Leibniz ScienceCampi – as well as with industry and other partners at home and abroad. They are subject to a transparent, independent evaluation procedure. Because of their importance for the country as a whole, the Leibniz Association Institutes are funded jointly by Germany’s central and regional governments. The Leibniz Institutes employ around 20,500 people, including 11,500 researchers. The financial volume amounts to 2 billion euros.
Leibniz Section E - "Environmental Sciences"- Environment and Sustainable Development
The research conducted at the institutes within the section “Environmental Sciences” is geared towards a better understanding of the Earth system, in each of three domains hydrosphere, lithosphere and atmosphere. The focus is on the interfaces at which these spheres most closely intertwine with human activities, which is in the troposphere, coastal waters and shelf seas, inland waters, agricultural systems and landscapes. As a cross-sectional task research on climate impacts and climate change plays an important role within the section.

Leibniz-Labs
The Leibniz Centre for Tropical Marine Research (ZMT) is a member of one of the new Leibniz Labs, in which Leibniz institutes work together on an interdisciplinary basis and with stakeholders from society, politics and business in order to develop practical solutions for major societal challenges. ZMT is part of the Leibniz Lab "Systemic Sustainability - Biodiversity, Climate, Agriculture and Nutrition within Planetary Boundaries" to which the inistitute will contribute its interdisciplinary expertise in research on tropical coastal ecosystems from a natural and social science perspective. With the new "Leibniz Labs" format, the Leibniz Association is strengthening its interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary excellence. In a separate project, the three newly-funded Leibniz Labs will be accopanied by a special project allowing for networking and reflection in order foster knowledge for future community initiatives.
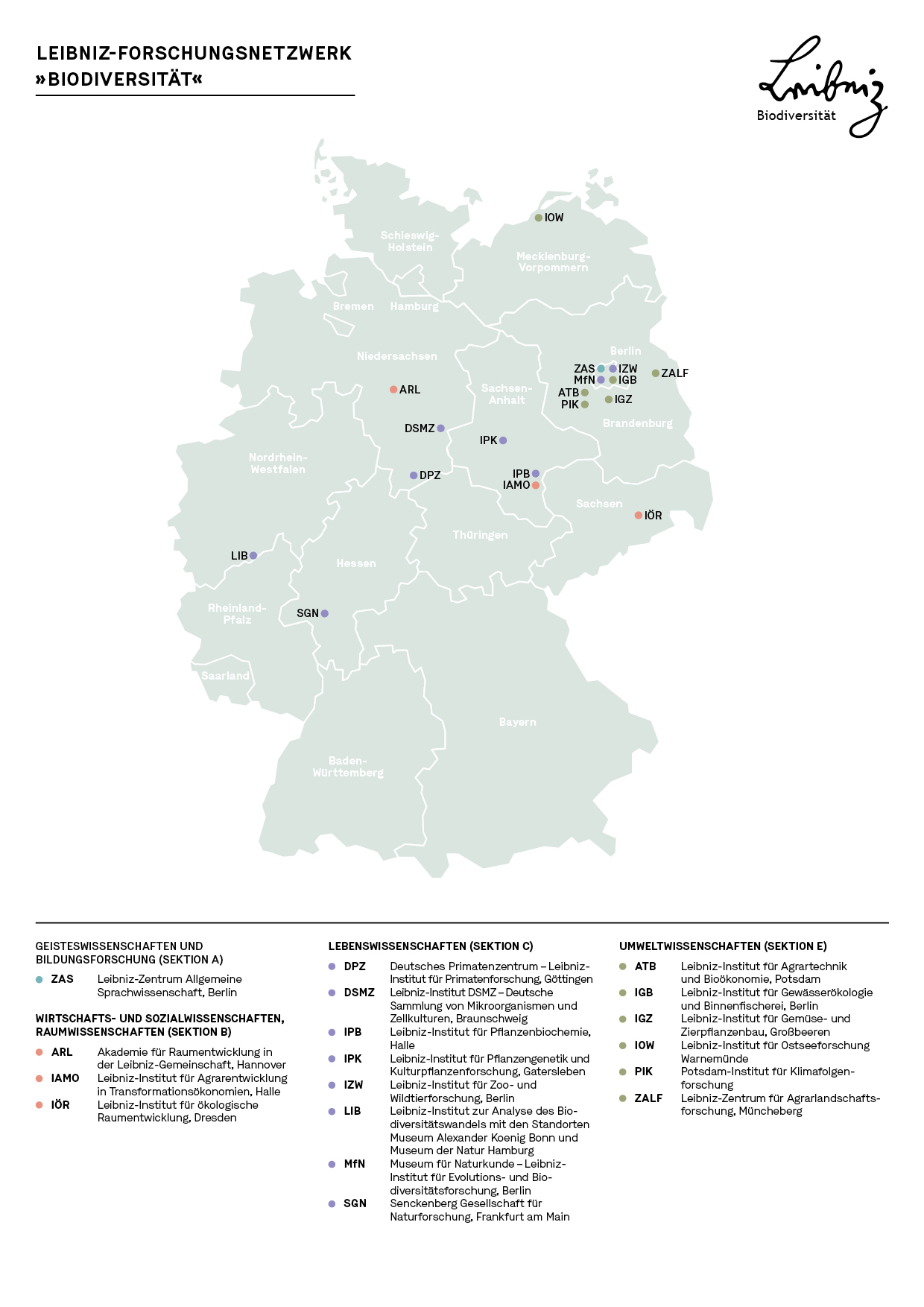
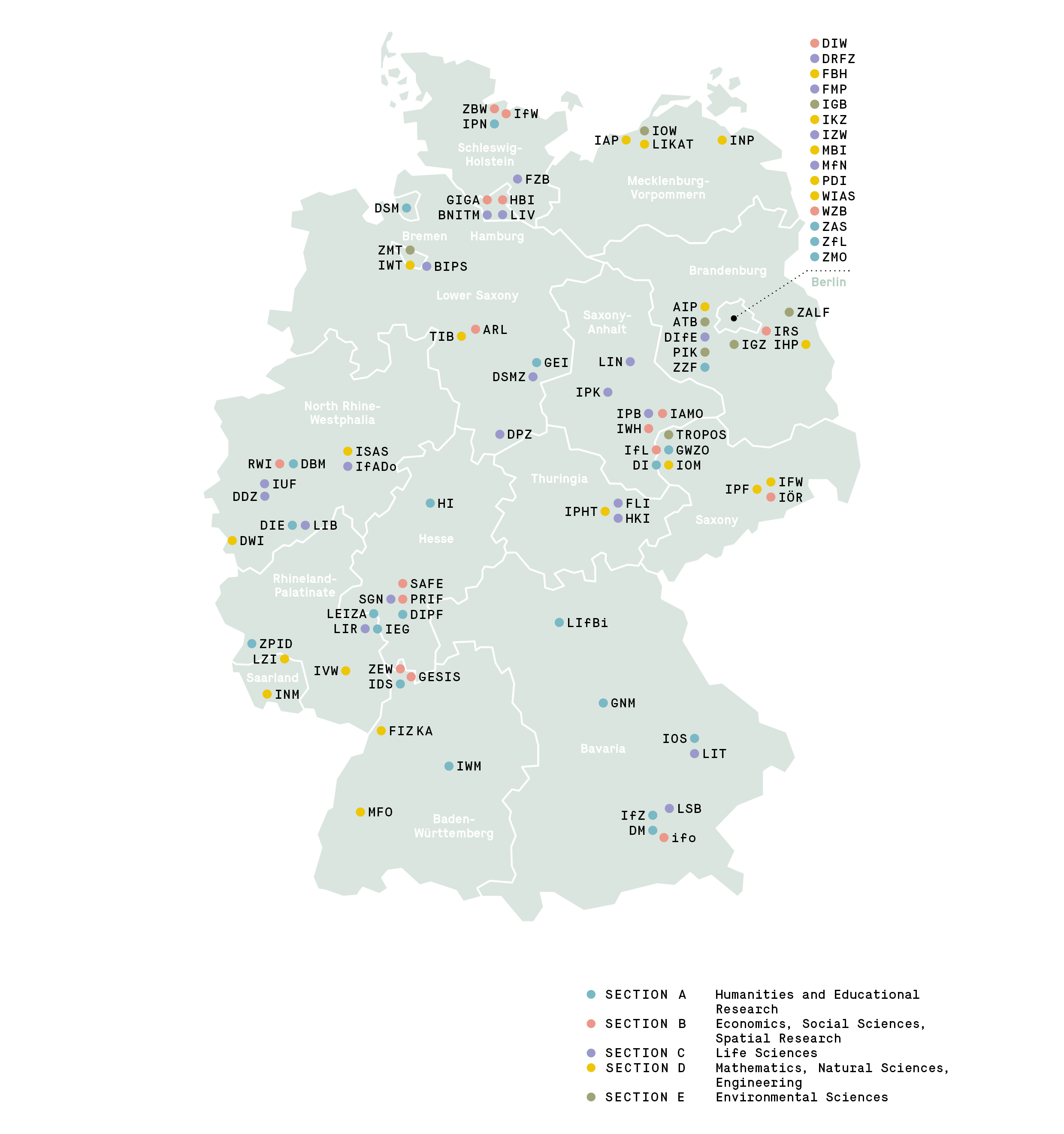
Leibniz Research Network Biodiversity
The Leibniz Research Network Biodiversity bundles and networks the expertise of 19 Leibniz institutions in the environmental, life, spatial, social, humanities and economic sciences.
The scientists at the participating institutions record and explore the biological diversity of life and develop socially relevant solutions for the protection and sustainable use of biodiversity through interdisciplinary research. Access to genetic resources and equitable benefit sharing (ABS) are also addressed. Equally, the Leibniz Biodiversity members are committed to the knowledge transfer to politics and society in order to raise awareness of the progressive loss of biodiversity and to strengthen its overall appreciation in society.
Link to Leibniz Research Network Biodiversity: https://www.leibniz-biodiversitaet.de/en/
Link to newsletter of the Leibniz Research Network Biodiversity: https://www.leibniz-biodiversitaet.de/en/mainnavigation/news/translate-to-english-neues-aus-dem-netzwerk-1/translate-to-english-newsletter-leibniz-biodiversitaet
Leibniz Research Network "Environmental Crisis - Crisis Environments (CrisEn)"
The Leibniz-Research-Network “Environmental Crises – Crisis Environments” is dedicated to the research of the perception and governance of environmental changes as crisis. A key to detect a crisis and to initiate political crisis management is the perception of a threat as urgent, existential, and uncertain in its consequences. Taking this as a vantage point, the Leibniz Research Network examines under which conditions environmental change is perceived and contested as crisis, and which governance arrangements foster effective and sustainable crisis management. Both steps are important as the attribution of environmental changes as crises involves biophysical and societal phenomena whose interaction are not well understood so far. Furthermore, these two perspectives on environmental crises include furthering the resilience of contemporary societies with regard to environmental changes as well as an understanding of crisis scenarios as an opportunity for sustainability transformations.
Leibniz Research Network "Earth & Societies"
Humankind is increasingly influencing the Earth system that has evolved over millions of years. Visible signs of this "Anthropocene" are global warming, pollution of the oceans and the decline in biodiversity. In the coming years, therefore, societal decisions of civilisation-historical significance will have to be made. A fundamental question is: How can the Earth system be ecologically stabilised in such a way that well-being, prosperity, justice, peace and security for all people are secured or even achieved?Against this background, the Leibniz Research Network "Earth & Societies" has set itself the task of gaining knowledge about people in the Earth system that is relevant to society's actions. Above all, the ecological carrying capacities of the Earth system are to be determined and sustainable development paths derived from them. On the one hand, the network develops innovative principles of integrated Earth system research. On the other hand, it is investigating the oceans and their use, biodiversity, environmental migration, urban-rural relationships and the potential of the bioeconomy from the perspective of the Earth system. Climate change is considered throughout.
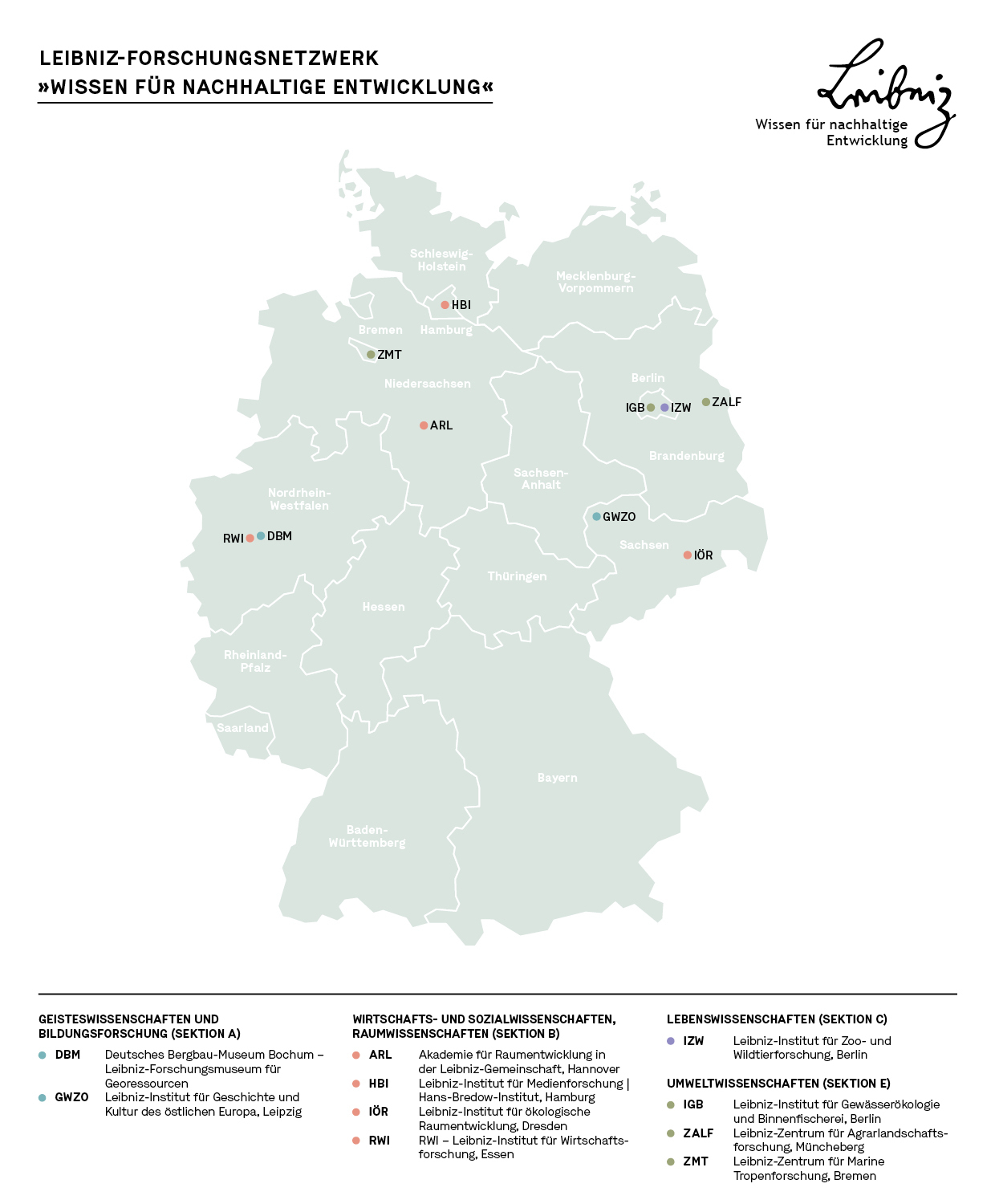
Leibniz Research Network „Knowledge for Sustainable Development"
By formulating the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in 2015, the global community agreed on an agenda for tackling humanity's most urgent challenges. Science has a key role to play in this: it provides the basis for understanding the complex processes and develops new knowledge, technological, social and ecological innovations together with actors from politics, business and society. The Leibniz Research Network "Knowledge for Sustainable Development" supports researchers in answering the associated theoretical and methodological questions. It brings togther and connects relevant research competencies in the Leibniz Association and contributes to the effectiveness and visibility of research for sustainable development. To this end, the network organises synthesis workshops, international conferences and summer schools in cooperation with other Leibniz institutions and external partners from science and practice, as well as future dialogues with influential personalities from politics, business and society.
Leibniz Research Alliance "Advanced Materials Safety"
Advanced materials are key to the creation of innovative products and technologies ranging from catalysis, green hydrogen generation, energy storage to biomedical applications. These applications require materials which combine different nanoscopic and/or microscopic building blocks, e.g., doped and core-shell nanoparticles and high-performance fibres, into hierarchical hybrid materials. This combination of micro- and nanoscale sized building blocks as well as the compositional material heterogeneity can impose new risks during their life cycle, e.g., by decomposition into different nanoparticles, microplastic or hybrid components and subsequent release of harmful constituents. To ensure sustainable innovations, the potential risks imposed by such complex materials need to be identified and understood timely over the whole production-application cycle up to the end of their life cycle.
![]()
German Marine Research Alliance (Deutsche Allianz für Meeresforschung - DAM)
The German Marine Research Alliance (Deutsche Allianz Meeresforschung - DAM) brings together leading German marine research institutions that contribute to the sustainable management of the oceans and seas with top-level research. The alliance addresses major future issues in marine research through joint research missions at the highest level. To this end, existing and new infrastructures, technologies and information systems are further developed and expanded. Together, science-based options for action for sustainable management of the oceans and seas are developed and communicated to society and politics. With the establishment of the German Marine Research Alliance, the Federal Government, the Northern-German Länder of Bremen, Hamburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Lower Saxony and Schleswig-Holstein, together with German marine and maritime research institutions, are sending a clear signal. They are positioning Germany as one of the leading nations in the successful implementation of the UN Decade of Marine Research for Sustainable Development (2021-2030).

German Marine Research Consortium - KDM
KDM brings together the marine science expertise of its member institutions and collectively presents it to policy makers and research funding organisations as well as to the general public. , marine research serves as a stimulus for innovation and contributes significantly to the standing of the maritime sector in the northern German coastal states through research work, contributions to higher education as well as through knowledge and technology transfer.

U Bremen Research Alliance
In April 2016, the U Bremen Research Alliance was founded by the University of Bremen and the ten non-university research institutes funded by the Federal Government and the Länder. The Alliance defines itself as promoter of scientific collaboration with low bureaucracy and short reporting lines. It is geared to researching major cross-institutional research topics. The essence of “U Bremen Research Alliance” lies in the sharing of infrastructures, excellent service and advisory structures, tailored career paths, and swift implementation of scientific ideas.

NFDI4Biodiversity – NFDI Consortium for Biodiversity, Ecology and Environmental Data
NFDI4Biodiversity is a consortium under the umbrella of the National Research Data Infrastructure (NFDI) dedicated to the mobilising biodiversity and environmental data for collective use.
The partners pool their scientific and technical expertise to provide a broad service portfolio for handling biodiversity and environmental data and to develop it further in close cooperation with users from research and practice. The consortium consists of Partners include close to 50 scientific institutions, museums, natural history societies, state offices, and other institutes and expert groups.
The cooperation of the partner network is guided by the knowledge that stakeholders in science, politics, nature conservation and landscape management need reliable data to be able to develop better contributions to the conservation of biodiversity.
ZMT will provide unique long-term time series from tropical regions. These will contribute to the research data management infrastructure by providing curation capacities. ZMT is also involved in Task Areas TA1 und TA4.
Northwest Marine Research Association - NWVM
This alliance of marine research institutions in the north-western region of Germany aims to foster the application of research results and the development of marine technologies and to perform research and transfer projects jointly with the business sector.
German Commission for Research Diving - KFT
A professional organisation of German research institutions, which perform scientific diving in accordance with the national regulations. This is the central platform for all issues related to scientific diving in Germany.
GFBio - Gesellschaft für Biologische Daten e.V.
The association GFBio e.V. is committed to the standardisation and sustainable management of research data from biology, ecology and environmental sciences. As a national contact point, the association's services and advice cover all steps in the "life cycle" of research data - from the collection of data to archiving and publication. GFBio has also established itself as a diverse forum for networking and helping to shape future developments in the field of research data management
House of Science - Haus der Wissenschaft (HdW) in Bremen
The House of Science in Bremen's city centre is designed to promote the understanding and appreciation of science to the general public in and around Bremen. It offers exhibitions, discussion panels, talks and other events concerning information on current research.

bremen digitalmedia is the interest group for media and information technology companies in the state of Bremen. Since 2009, the non-profit association bremen digitalmedia has been specifically committed to education and training in the field of IT and media. The industry association bremen digitalmedia e.V. was founded in 1997 – at that time under the name bremen multimedial - as an initiative for the promotion, development, application and distribution of interactive media in the economic region of Bremen.
Partnerships with the following institutions

Zoo Berlin
Protection and preservation of biodiversity and the sustainable use of marine resources are important aspects of the research work of the Leibniz Centre for Tropical Marine Research (ZMT), working with like-minded people is a declared goal.






